FireCAD : Fire Tube Boiler Design Software
Fire Tube Boiler Design Software
Fire Tube Boiler Design Software – FireCAD
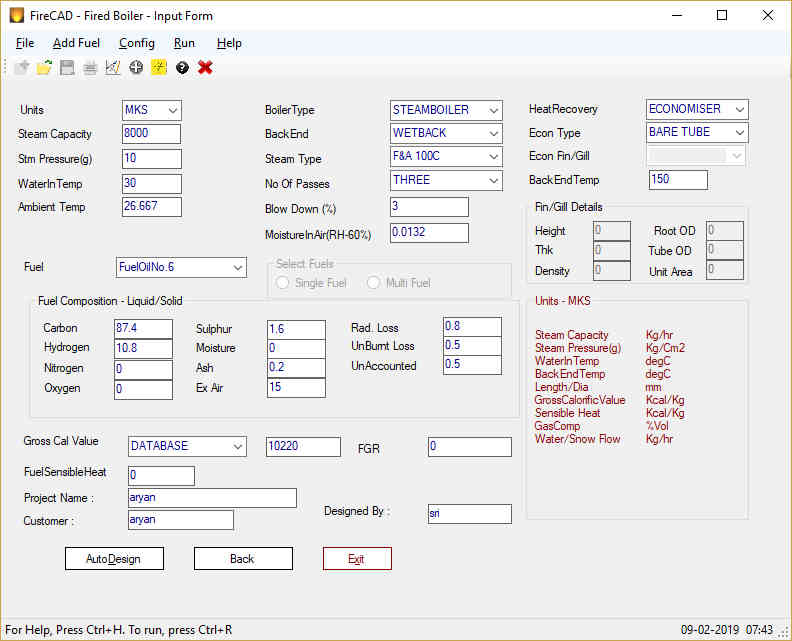
FireCAD is a comprehensive software solution for designing a wide range of fire tube boilers, including package boilers, waste heat recovery boilers, and hot water generators. Whether you’re a seasoned engineer or just starting out, FireCAD provides the tools you need for quick, accurate, and optimized designs.
Capabilities:
- Versatile Design: Create designs for oil, gas, coal, biomass, and other solid fuel-fired boilers.
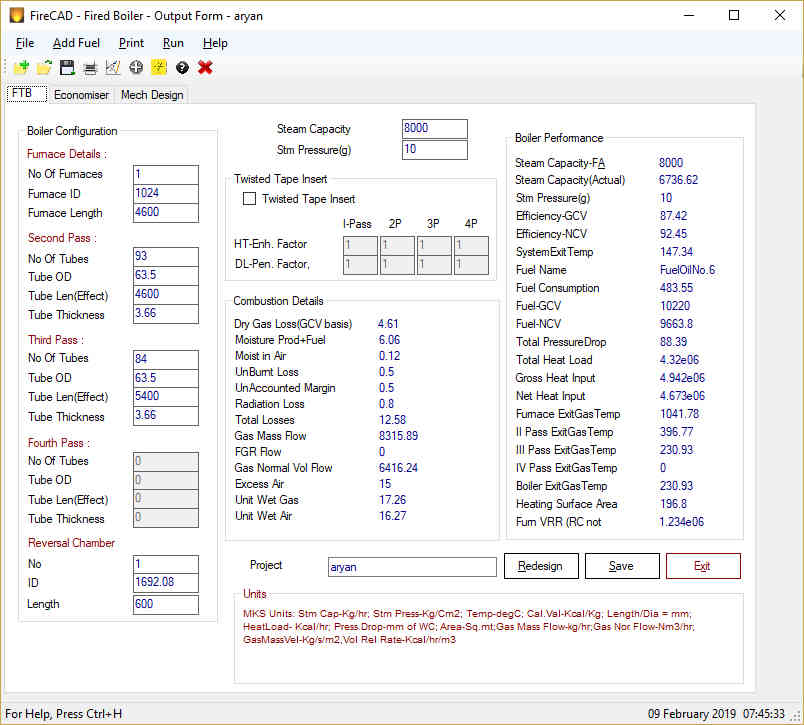
- Comprehensive Configurations: Design 2, 3, and 4-pass boilers with wet back or dry back configurations.
- Waste Heat Recovery: Develop efficient waste heat recovery boilers for various applications, including chemical plants, DG sets, process industries, metallurgical plants, and power plants.
- Hot Water Generation: Design both fired and unfired hot water generators.
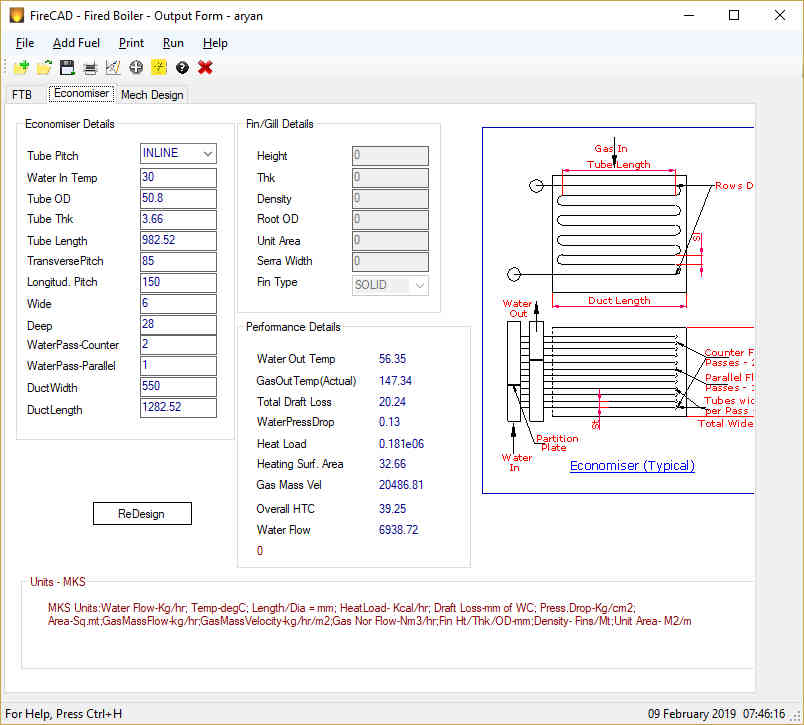
- Economizer Integration: Include economizers with bare, finned, or gilled tubes to maximize efficiency.
- Shell Diameter Calculation: Easily calculate shell diameters for integral steam space and elevated drum type boilers.
Features:
- AutoDesign: Achieve optimized designs with the automated design feature.
- Extensive Fuel Database: Access a vast library of fuel data, with the ability to add custom fuels and waste gases.
- Expert Guidance: Benefit from built-in help resources that provide design methodologies, tips, and best engineering practices.
- Detailed Reporting: Generate comprehensive design reports with printing options.
- Flexible Units: Work in MKS, SI, or FPS units.
FireCAD empowers you to:
- Streamline your design process: Intuitive tools and automated features save you time and effort.
- Improve accuracy: Built-in checks and calculations minimize errors.
- Optimize performance: Design efficient and reliable boilers that meet your specific needs.
- Explore various configurations: Easily analyze different boiler types and configurations to find the best solution.

Fire Tube Boilers: A Robust and Reliable Steam Solution
Fire tube boilers are a classic and proven technology for steam generation, known for their robust construction and simple operation. Unlike water tube boilers, where water flows through tubes surrounded by hot gases, fire tube boilers contain water within a shell while hot gases pass through internal tubes.
How Fire Tube Boilers Work:
Fuel, such as oil, gas, or solid fuels like coal or biomass, is burned in a furnace within the boiler shell. The hot combustion gases then travel through tubes that are submerged in water. This efficient heat transfer process generates steam, which is collected in the steam space above the water level.
Key Features and Configurations:
- Furnace: A cylindrical structure that houses the combustion process. Furnaces can be plain or corrugated to accommodate thermal expansion.
- Gas Passes: The hot gases pass through multiple tubes (typically 2, 3, or 4 passes) to maximize heat transfer and improve efficiency.
- Wet Back vs. Dry Back: Wet back boilers have a water-cooled rear chamber (reversible chamber), while dry back boilers have a refractory-lined chamber.
- Integral Steam Space vs. Elevated Drum: Most fire tube boilers have an integral steam space within the shell. Larger capacity boilers may utilize an elevated drum connected by risers and downcomers.
- Twin Furnace: For higher capacity requirements, some boilers feature twin furnaces to increase steam production.
Advantages of Fire Tube Boilers:
- Robust Construction: Simple design and durable materials ensure long-lasting performance.
- Easy Operation and Maintenance: Straightforward operation and accessible components simplify maintenance tasks.
- Compact Footprint: Space-saving design is ideal for various installations.
- Cost-Effective: Generally less expensive than water tube boilers, especially for lower capacity requirements.
- Wide Fuel Flexibility: Can be designed to burn a variety of fuels, including oil, gas, and solid fuels.
Applications:
Fire tube boilers are widely used in industries such as:
- Food processing
- Textiles
- Chemicals
- Pharmaceuticals
- Heating systems